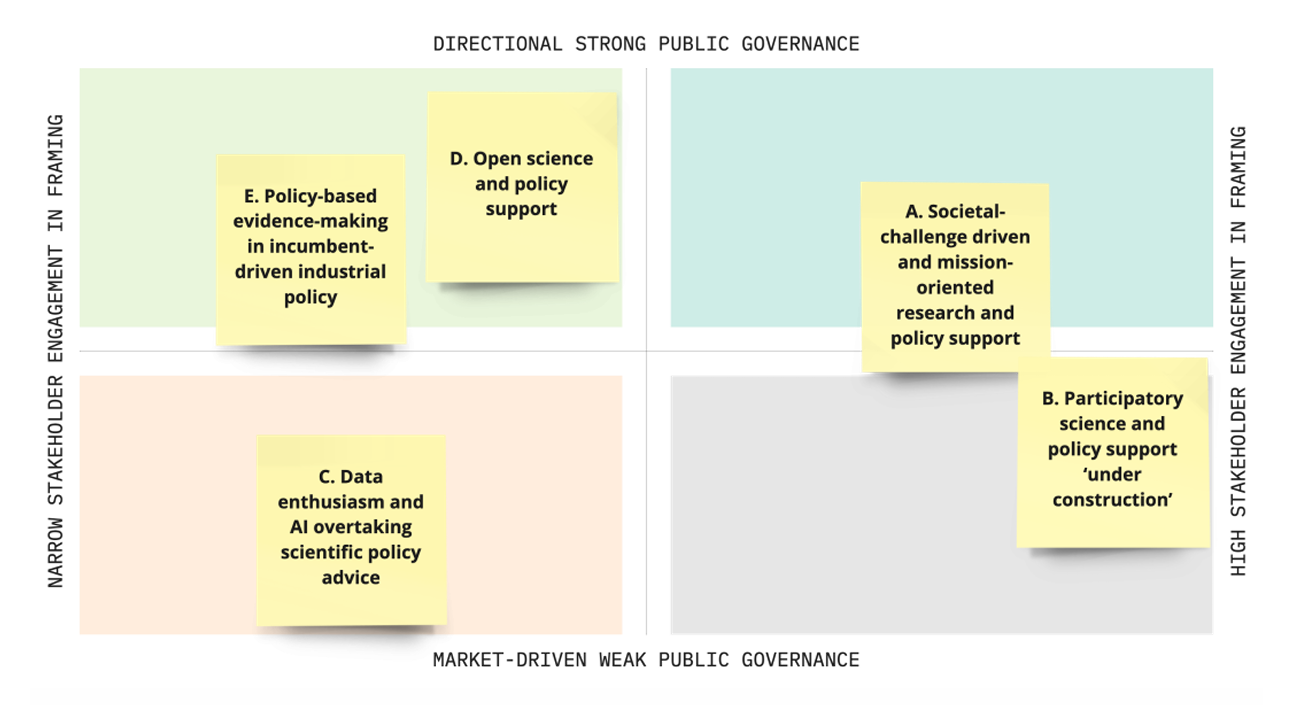
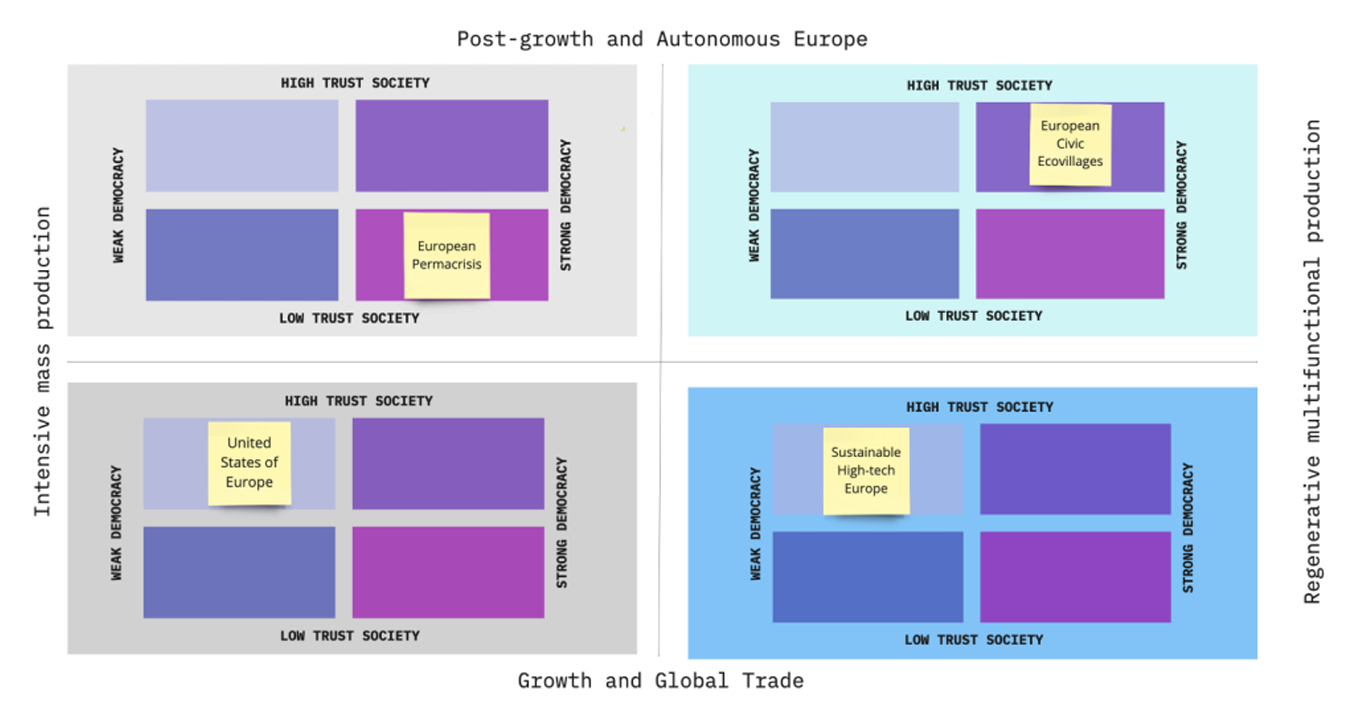
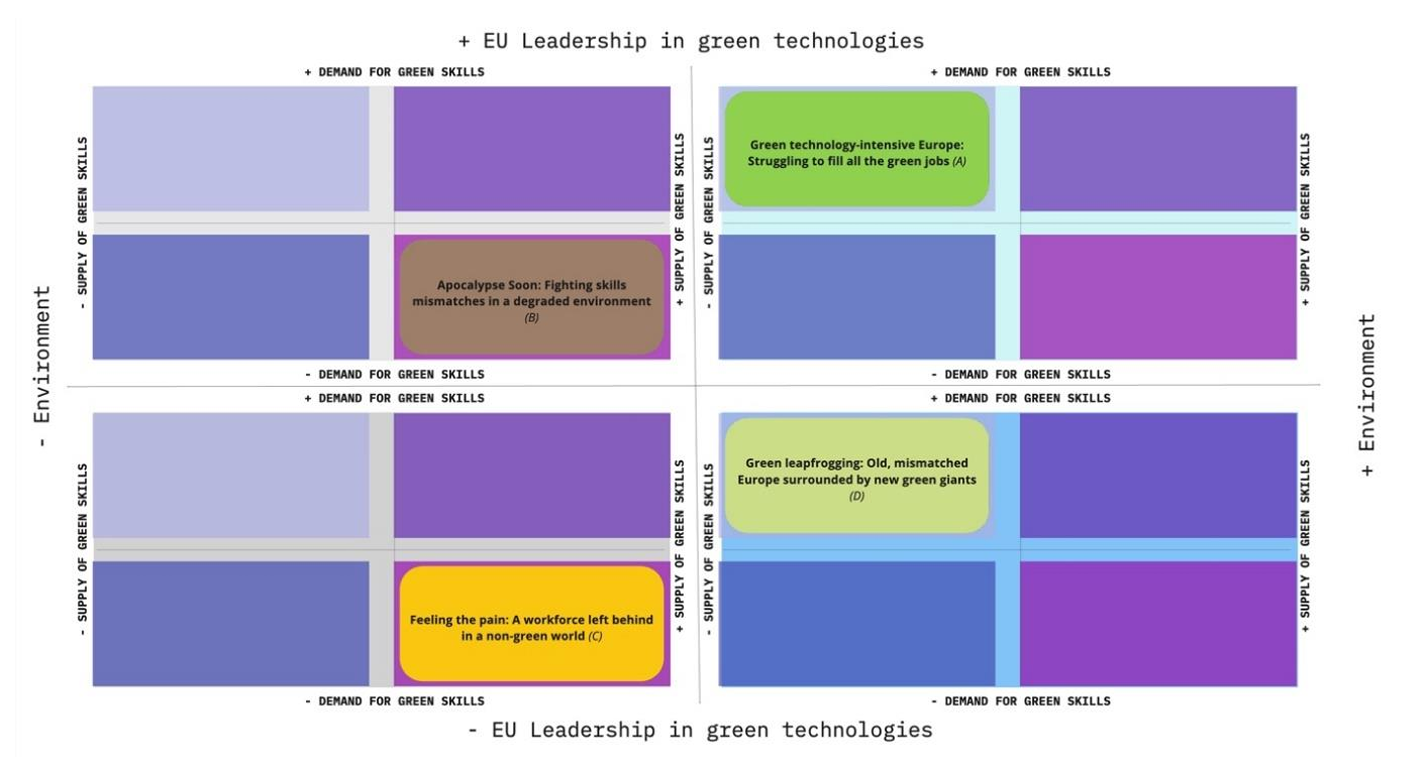
Insight Foresight Institute’s CEO, Totti Könnölä, supported by the experts Ferdinando Boero, Denis Lacroix, Andreas Ligtvoet and Evangelos Papathanasiou and 4Strat, led the foresight project “Support to the Mission Board Healthy Oceans, Seas, Coastal and Inland Waters”, developed by the Foresight on Demand consortium for the Directorate-General for Research and Innovation of the European Commission.

Using foresight methodologies — including horizon scanning, weak-signal detection and a real-time Delphi study — the team identified five focal areas representing alternative but interconnected pathways for action:
- Climate-resilient coastlines: adapting to unavoidable sea-level rise and extreme weather events across Europe.
- Clean water for the blue planet: halving industrial nutrients, plastics, pharmaceuticals and pesticides in European waters by 2030.
- Vital aquatic ecosystems: harmonising ecology and economy in decision-making to protect biodiversity and sustainable productivity.
- Open digital twin of oceans and waters: integrating real-time data for observation, early warning and ecosystem management.
- Humans at sea: piloting sustainable living, aquatic production and circular design in semi-permanent floating structures.
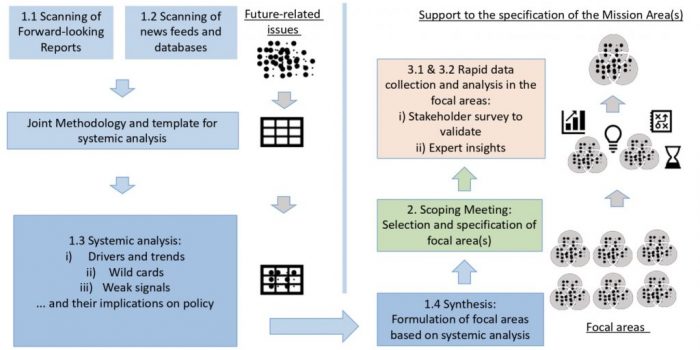
The Delphi results showed broad consensus on the urgency to restore water health and adopt an ecosystem-based governance approach. Participants emphasised the need to strengthen biodiversity research, improve coordination between marine and inland policies, and enhance monitoring of pollution sources.
Main recommendations:
- Adopt a holistic approach and promote water literacy across all sectors of society.
- Create multi-stakeholder networks using shared and accessible language that bridges inland and ocean waters.
- Develop integrated impact assessment and continuous monitoring systems to prevent unintended effects on complex ecosystems.
This work positions Europe as a global leader in achieving resilient coasts, clean waters and sustainable blue economies, aligning scientific foresight with tangible societal transformation.
Further information
Totti Könnölä, Ferdinando Boero, Denis Lacroix, Andreas Ligtvoet, Evangelos Papathanasiou
“Mission Area: Healthy Oceans, Seas and Coastal and Inland Waters – Foresight on Demand Brief in Support of the Horizon Europe Mission Board.”European Commission – Directorate-General for Research and Innovation, Foresight on Demand series. Publications Office of the European Union, 2021. ISBN 978-92-76-41537-4.