The European Commission expert panel applied the entrepreneurial innovation ecosystem model developed by IFI in expert advice in Montenegro. In this assignment, Totti Könnölä, CEO if IFI, was the rapporteur of the panel that was set up to provide external advice and operational recommendations on how the country could develop its entrepreneurial innovation ecosystem.
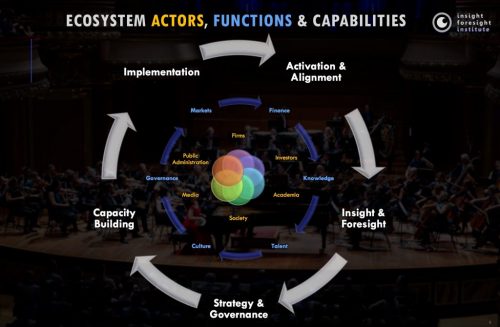
The expert panel provided advice on the necessary legislative changes, the design of a functional entrepreneurial innovation and startup support ecosystem model and the necessary funding schemes for startups and other actors of the ecosystem.
For more information
The Commission project website
The final report available here for free
 Juan Mulet Melia, a member of the Innovation Council of IFI, and Totti Könnölä, CEO of the Insight Foresight Institute (IFI), write in Cinco Días, one of the leading economic journals in Spain, to promote smart specialization in the regions.
Juan Mulet Melia, a member of the Innovation Council of IFI, and Totti Könnölä, CEO of the Insight Foresight Institute (IFI), write in Cinco Días, one of the leading economic journals in Spain, to promote smart specialization in the regions.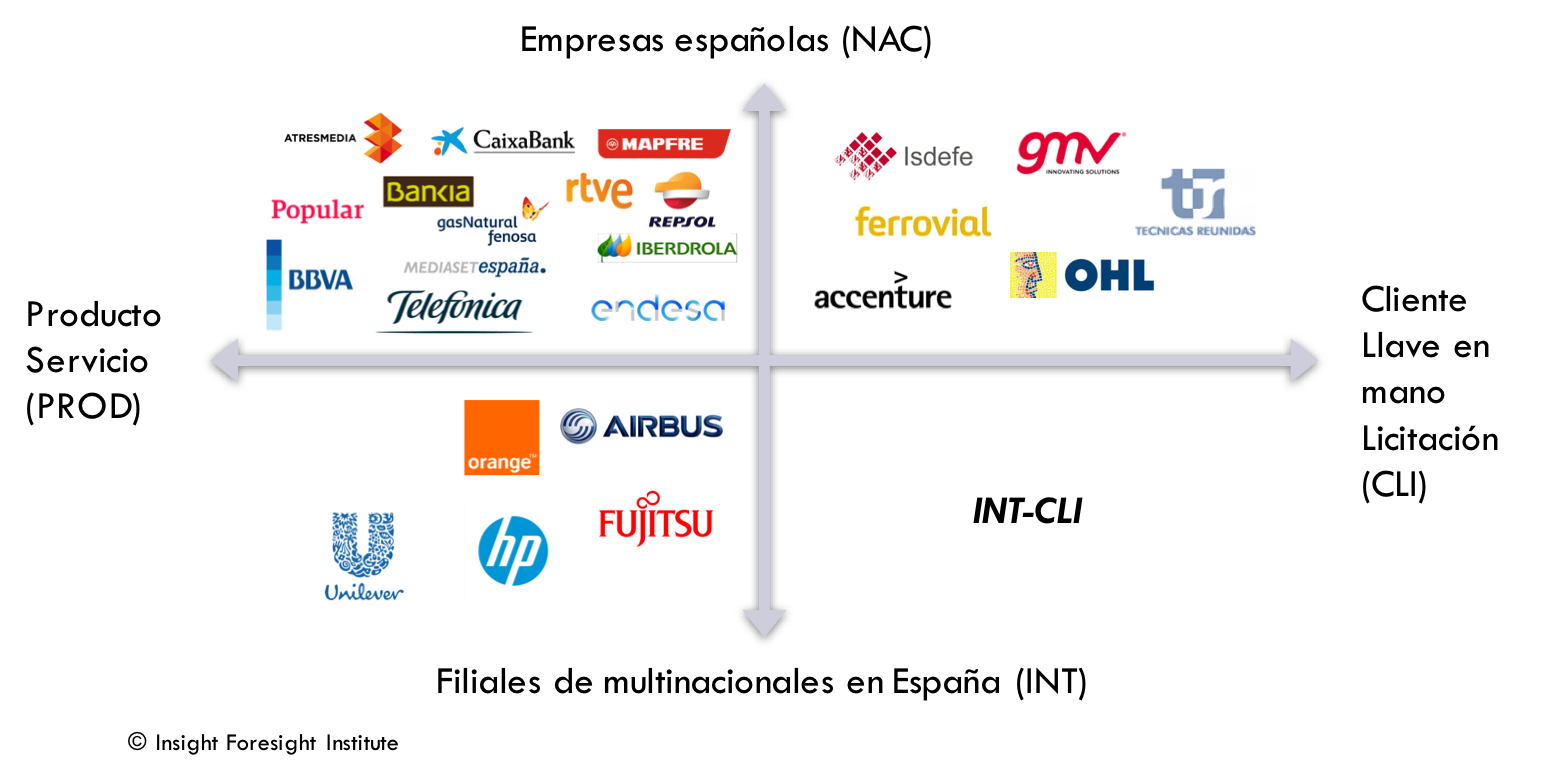
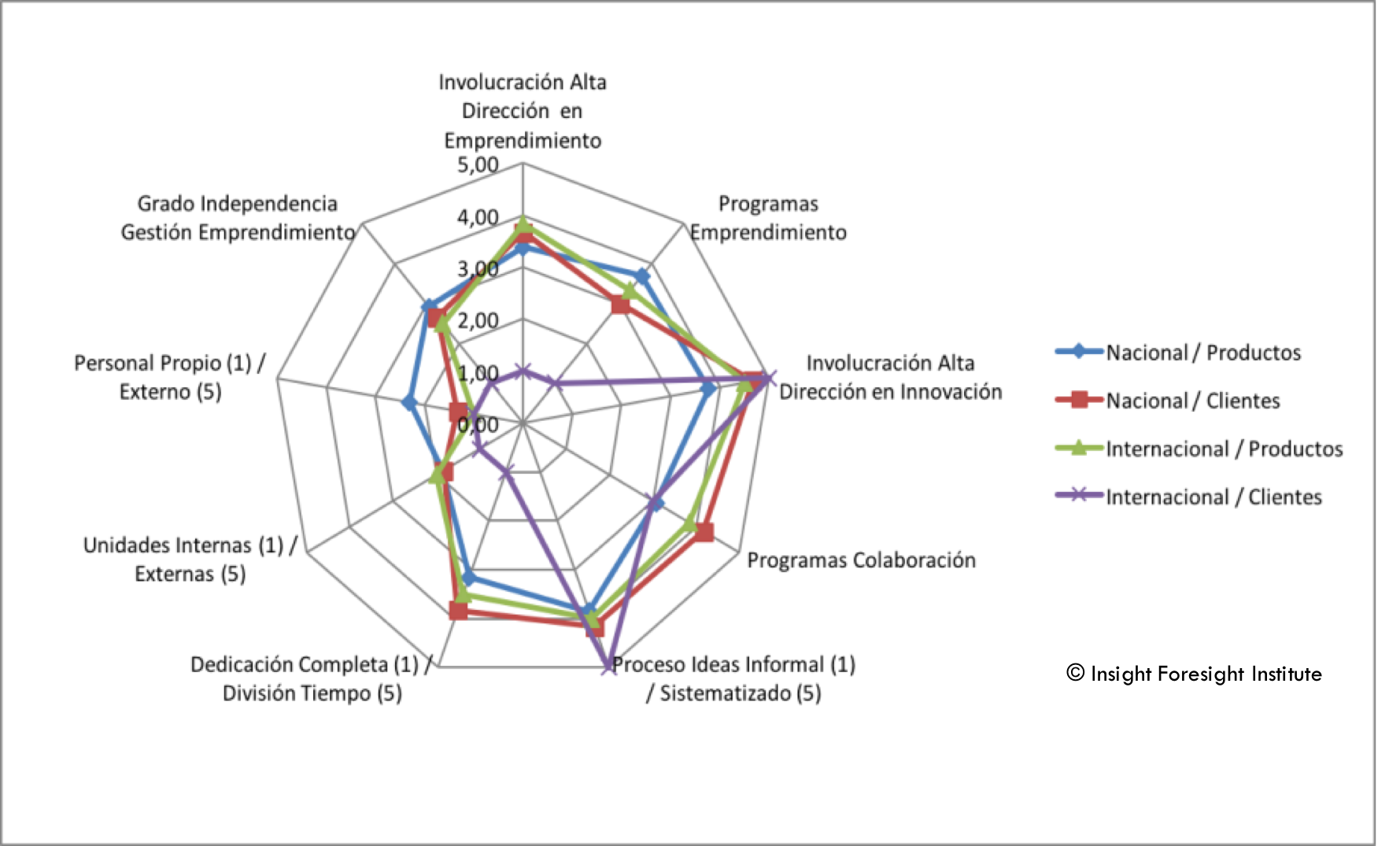

 Juan Mulet, the member of IFI Innovation Council writes in Cinco Dias, one of the leading economic daily papers in Spain on how innovation, purchase and employment are, or should be, connected.
Juan Mulet, the member of IFI Innovation Council writes in Cinco Dias, one of the leading economic daily papers in Spain on how innovation, purchase and employment are, or should be, connected.